比特币 mining puzzle 是计算密集型,以太坊设计了 memory hard mining puzzle,限制了 ASIC 芯片的使用。
以太坊账户模型天然能防御 double-spending attack(花钱的人不诚实)。以太坊用 nonce(实际起到计数器作用)防止 replay attack(收钱的人不诚实)。
外部账户要素:balance,nonce。
合约账户要素:balance,nonce(记录调用其它合约的次数),code,storage。
以太坊智能合约的使用特点要求参与者的身份比较稳定;合约本身的地址更要稳定。
账户状态树#
记录以太坊所有账户状态的数据结构要能快速查找、更新、新增,同时要能提供 Merkle proof。
哈希表可以支持快速查找,但每次收到新区块中包含的交易都需要重新构建 Merkle tree,以太坊中的账户数目巨大,这一操作开销太大。
Merkle tree 不能支持快速查找和更新;排序的 Merkle tree 可以保证所有节点的 Merkle tree 一致,但新增的账户可能造成树的大规模重建,开销太大。
Trie 树可以支持快速查找、更新、新增。
- 以太坊 Trie 树的 branching factor 是 16+1(0-f 和一个结束标识);
- 以太坊的地址长度都是 40 个 16 进制的数,Trie 树的查找效率和 key 的长度相关;
- Trie 树不会出现碰撞;
- 同样的输入用任何顺序构建出来的 Trie 树都是相同的;
- Trie 树更新操作的局部性很好;
- 以太坊地址的分布稀疏,可能使 Trie 树退化成线性结构,导致效率降低。
Patricia tree 做了路径压缩,树变浅,访问内存的次数大大减少。
Merkle Patricia tree 用哈希指针替代普通指针,可以计算出根哈希值写在区块头中。
- MPT 可以证明 non-membership:给出如果存在的话应该所在的分支,将其作为 Merkle proof 发布出去,作为存在对应账户的证明。
以太坊实际采用 Modified MPT。
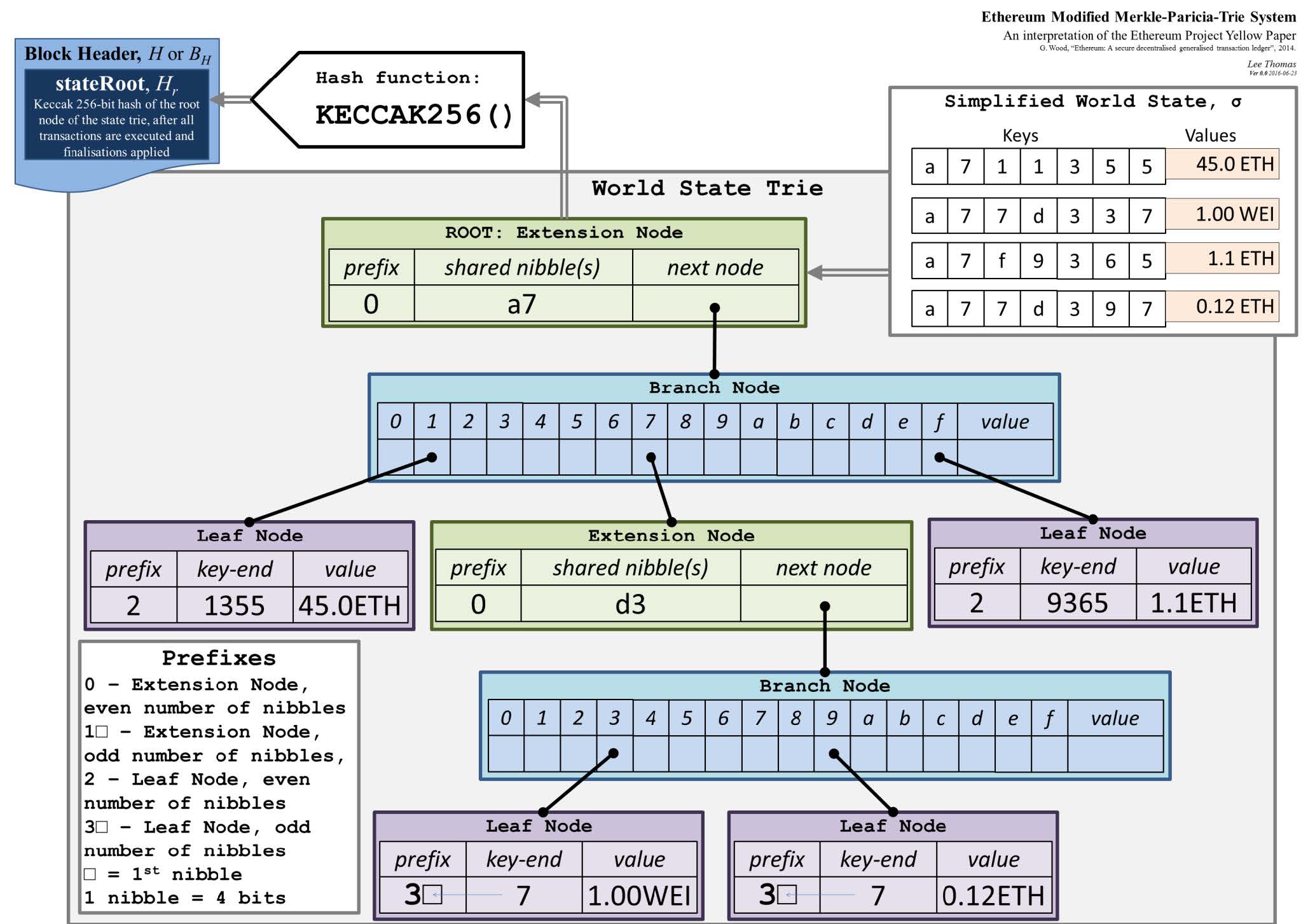
- 1 nibble 就是一个 16 进制数;分奇数个 nibble 和偶数个 nibble。
- 有 extension node 和 branch node。
发布新区块后,状态树中的部分节点值会被更新;更新在新的分支上进行,原来的状态被保留下来。
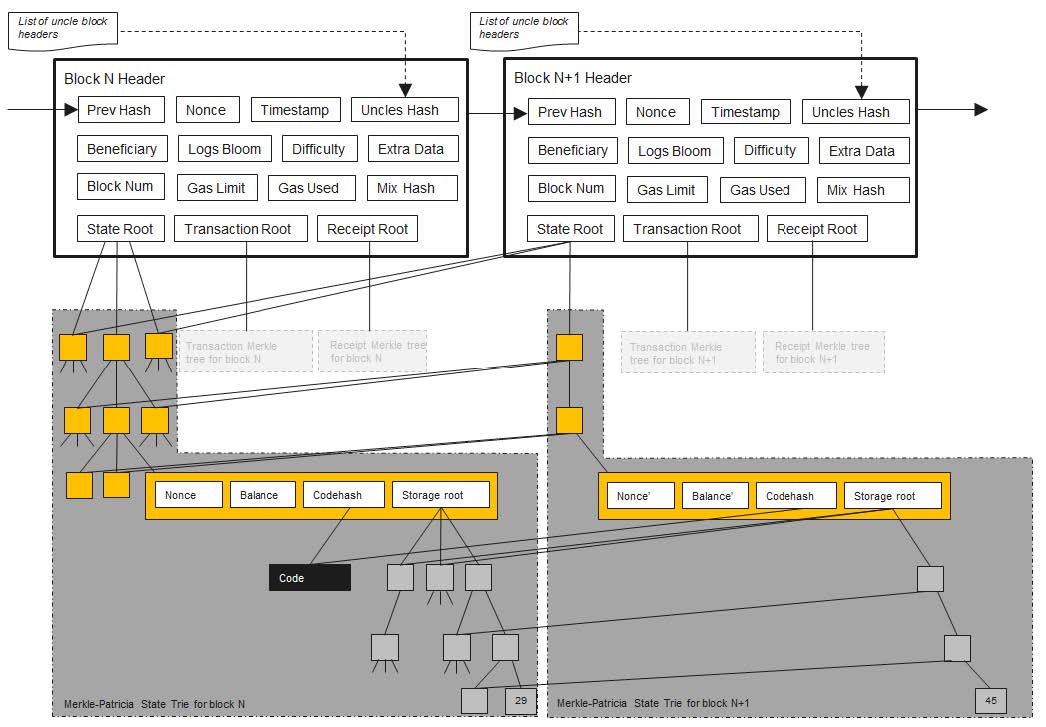
- 每个合约账户的存储也是一棵 MPT(storage root),维护变量和变量取值的映射。
- 每次出现一个区块,节点都需要新建一棵 MPT,其中大部分的节点是共享的(右边节点指向左边节点的连线),少部分发生变化的节点需要新建分支。
- 保留原来的状态是为了交易回滚。
- 以太坊的出块时间短,state fork 是常态。
- 以太坊的智能合约逻辑可以很复杂,无法简单推算出合约执行前的状态。
账户的状态经过 RLP(Recursive Length Prefix)序列化处理后存储在 MPT 中。
RLP 特点是极简,只支持 nested array of bytes,复杂的序列化操作都由应用层处理。
状态树必须包含所有账户,不能只包含当前区块中的交易涉及的账户,原因是以太坊采用基于账户的模型,需要能快速查询到某个账户的余额,若状态树不完整,则必须向前回溯(这样就和 UTXO 模型类似了),如果是新的收款地址,则必须回溯到创世块。
交易树和收据树#
每发布一个区块,该区块中包含的交易组织成一棵交易树,每个交易执行完后形成一个收据,记录交易的相关信息。
- 交易树和收据树都是 MPT,它们的节点一一对应。
- 利用收据树可以快速查询交易的执行结果。
- 交易树可以提供区块中存在某笔交易的 Merkle proof,收据树可以提供某个交易执行结果的 Merkle proof。
bloom filter 用于快速判断某个元素是否在一个较大的集合中,具体做法是对集合中的每个元素计算摘要,映射到紧凑的包含 n 个二进制位的向量中,向量的所有位的初始值是 0,映射到的位置的值置为 1。
- bloom filter 可能误报(false positive)不会漏报。
- bloom filter 可以采用一组哈希函数,分别进行映射,以降低碰撞(误报)的概率。
- 一般 bloom filter 不支持删除操作,要支持删除需要将存在映射的标识位改为计数器,同时要考虑溢出,数据结构变复杂,和设计 bloom filter 的初衷违背。
每个交易的收据里包含一个 bloom filter,记录交易的类型、地址等信息;发布的区块的块头里有一个总的 bloom filter,是区块里所有交易的 bloom filter 的并集。
- 使用场景:查找过去十天跟某个智能合约相关的所有交易。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
| // https://github.com/ethereum/go-ethereum/blob/v1.10.11/core/types/block.go#L185
// NewBlock creates a new block. The input data is copied,
// changes to header and to the field values will not affect the
// block.
//
// The values of TxHash, UncleHash, ReceiptHash and Bloom in header
// are ignored and set to values derived from the given txs, uncles
// and receipts.
func NewBlock(header *Header, txs []*Transaction, uncles []*Header, receipts []*Receipt, hasher TrieHasher) *Block {
b := &Block{header: CopyHeader(header), td: new(big.Int)}
// TODO: panic if len(txs) != len(receipts)
if len(txs) == 0 {
b.header.TxHash = EmptyRootHash
} else {
b.header.TxHash = DeriveSha(Transactions(txs), hasher)
b.transactions = make(Transactions, len(txs))
copy(b.transactions, txs)
}
if len(receipts) == 0 {
b.header.ReceiptHash = EmptyRootHash
} else {
b.header.ReceiptHash = DeriveSha(Receipts(receipts), hasher)
b.header.Bloom = CreateBloom(receipts)
}
if len(uncles) == 0 {
b.header.UncleHash = EmptyUncleHash
} else {
b.header.UncleHash = CalcUncleHash(uncles)
b.uncles = make([]*Header, len(uncles))
for i := range uncles {
b.uncles[i] = CopyHeader(uncles[i])
}
}
return b
}
// https://github.com/ethereum/go-ethereum/blob/v1.10.11/trie/trie.go#L57
// Trie is a Merkle Patricia Trie.
// The zero value is an empty trie with no database.
// Use New to create a trie that sits on top of a database.
//
// Trie is not safe for concurrent use.
type Trie struct {
db *Database
root node
// Keep track of the number leafs which have been inserted since the last
// hashing operation. This number will not directly map to the number of
// actually unhashed nodes
unhashed int
}
// https://github.com/ethereum/go-ethereum/blob/v1.10.11/core/types/receipt.go#L52
// Receipt represents the results of a transaction.
type Receipt struct {
// Consensus fields: These fields are defined by the Yellow Paper
Type uint8 `json:"type,omitempty"`
PostState []byte `json:"root"`
Status uint64 `json:"status"`
CumulativeGasUsed uint64 `json:"cumulativeGasUsed" gencodec:"required"`
// Bloom 根据 Logs 产生出来
Bloom Bloom `json:"logsBloom" gencodec:"required"`
Logs []*Log `json:"logs" gencodec:"required"`
// Implementation fields: These fields are added by geth when processing a transaction.
// They are stored in the chain database.
TxHash common.Hash `json:"transactionHash" gencodec:"required"`
ContractAddress common.Address `json:"contractAddress"`
GasUsed uint64 `json:"gasUsed" gencodec:"required"`
// Inclusion information: These fields provide information about the inclusion of the
// transaction corresponding to this receipt.
BlockHash common.Hash `json:"blockHash,omitempty"`
BlockNumber *big.Int `json:"blockNumber,omitempty"`
TransactionIndex uint `json:"transactionIndex"`
}
// https://github.com/ethereum/go-ethereum/blob/v1.10.11/core/types/log.go#L29
// Log represents a contract log event. These events are generated by the LOG opcode and
// stored/indexed by the node.
type Log struct {
// Consensus fields:
// address of the contract that generated the event
Address common.Address `json:"address" gencodec:"required"`
// list of topics provided by the contract.
Topics []common.Hash `json:"topics" gencodec:"required"`
// supplied by the contract, usually ABI-encoded
Data []byte `json:"data" gencodec:"required"`
// Derived fields. These fields are filled in by the node
// but not secured by consensus.
// block in which the transaction was included
BlockNumber uint64 `json:"blockNumber"`
// hash of the transaction
TxHash common.Hash `json:"transactionHash" gencodec:"required"`
// index of the transaction in the block
TxIndex uint `json:"transactionIndex"`
// hash of the block in which the transaction was included
BlockHash common.Hash `json:"blockHash"`
// index of the log in the block
Index uint `json:"logIndex"`
// The Removed field is true if this log was reverted due to a chain reorganisation.
// You must pay attention to this field if you receive logs through a filter query.
Removed bool `json:"removed"`
}
// CreateBloom creates a bloom filter out of the give Receipts (+Logs)
func CreateBloom(receipts Receipts) Bloom {
buf := make([]byte, 6)
var bin Bloom
for _, receipt := range receipts {
for _, log := range receipt.Logs {
bin.add(log.Address.Bytes(), buf)
for _, b := range log.Topics {
bin.add(b[:], buf)
}
}
}
return bin
}
// add is internal version of Add, which takes a scratch buffer for reuse (needs to be at least 6 bytes)
func (b *Bloom) add(d []byte, buf []byte) {
i1, v1, i2, v2, i3, v3 := bloomValues(d, buf)
b[i1] |= v1
b[i2] |= v2
b[i3] |= v3
}
// bloomValues returns the bytes (index-value pairs) to set for the given data
func bloomValues(data []byte, hashbuf []byte) (uint, byte, uint, byte, uint, byte) {
sha := hasherPool.Get().(crypto.KeccakState)
sha.Reset()
sha.Write(data)
sha.Read(hashbuf)
hasherPool.Put(sha)
// The actual bits to flip
v1 := byte(1 << (hashbuf[1] & 0x7))
v2 := byte(1 << (hashbuf[3] & 0x7))
v3 := byte(1 << (hashbuf[5] & 0x7))
// The indices for the bytes to OR in
i1 := BloomByteLength - uint((binary.BigEndian.Uint16(hashbuf)&0x7ff)>>3) - 1 // 0x7ff 是 2047
i2 := BloomByteLength - uint((binary.BigEndian.Uint16(hashbuf[2:])&0x7ff)>>3) - 1
i3 := BloomByteLength - uint((binary.BigEndian.Uint16(hashbuf[4:])&0x7ff)>>3) - 1
return i1, v1, i2, v2, i3, v3
}
// BloomLookup is a convenience-method to check presence int he bloom filter
func BloomLookup(bin Bloom, topic bytesBacked) bool {
return bin.Test(topic.Bytes())
}
|
GHOST 共识#
以太坊出块时间十几秒,P2P flooding 传播区块的过程又较慢,很多节点可能没有收到最新区块,出现临时性的分叉是常态。
如果以太坊沿用比特币的共识机制,大型矿池相较于个体矿工的不成比例优势(centralization bias):出现等长分叉时,普通矿工倾向于沿着矿池挖出的最新区块所在的分叉链继续挖,因为矿池本身会沿着这条链挖,矿池的算力优势使得这条链成为最长合法链的概率比其它分叉链的大。
以太坊引入了 uncle block(叔父区块)机制:
- 原始版本中,最新区块可以把叔父区块包含进来,挖出叔父区块的节点可以获得 7/8 的区块奖励(但拿不到 gas fee),最新区块每包含一个叔父区块可以多获得 1/32 的区块奖励;一个区块最多可以包含 2 个叔父区块。
- 缺陷:只能包含 2 个叔父区块;最新区块出于竞争考虑可能恶意不包含叔父区块,损人不利己,但竞争对手的损失更大。
- 新版中,扩展了叔父区块的定义,不一定是当代叔父,可以是隔六代的叔父,即和当前区块在七代以内有共同的祖先。
- 最新区块恶意不包含叔父区块,最新区块的下一个区块、下下一个区块也可以包含,记账权不可能总是被同一个节点拿到。
- 叔父区块代数如果不加限制,全节点需要维护的叔父区块的状态会太多。限制在七代且奖惩递减,是鼓励出现分叉尽早合并,越早合并奖励越多。
- 最新区块每包含一个叔父区块可以多获得 1/32 的区块奖励,不论包含的是哪个辈分的叔父。
- 叔父区块中的交易不会被执行,也不做检查,只会检查叔父区块是否符合挖矿难度。
- 叔父区块只取分叉后的第一个区块,后面跟的一串区块不算叔父区块。如果后面跟的一串也算叔父区块,分叉攻击的成本就太低了,节点可以先抱着分叉的目的在叔父区块后面跟的一串区块后面挖矿,能成为最长合法链最好,即使不能成,一串区块也都能拿到叔父区块的奖励。这一机制也是鼓励出现分叉尽早合并。
▭ ← ▭ ← ▭ ← ▭ ← ▭ ← ▭ ← ▭
▭ ▭ ▭ ▭ ▭ ▭
2/8 3/8 4/8 5/8 6/8 7/8
挖矿算法 ethash#
比特币希望可以 one CPU, one vote。
抗 ASIC 芯片的 mining puzzle 的一个思路是增加对内存访问的需求,即 memory hard mining puzzle。
- ASIC 芯片访问内存的速度相对于普通计算机没有显著优势。
伪代码#
通过 seed 计算 cache:
1
2
3
4
5
| def mkcache(cache_size, seed):
o = [hash(seed)]
for i in range(1, cache_size):
o.append(hash(o[-1]))
return o
|
cache 中元素按顺序生成,第一个元素是 seed 的哈希,后面的每个元素是前一个元素的哈希。- 每隔 30,000 个区块会重新生成
seed(对原来的 seed 求哈希值),并且利用新的 seed 生成新的 cache。 cache 的初始大小为 16M,每隔 30,000 个区块重新生成时增大初始大小的 1/128 —— 128K。
通过 cache 来生成 dataset 中第 i 个元素:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| def calc_dataset_item(cache, i):
cache_size = cache.size
mix = hash(cache[i % cache_size] ^ i)
# 迭代 256 轮得到 64 字节的哈希值作为大数据集中的第 i 个元素
for j in range(256):
cache_index = get_int_from_item(mix) # 求 cache 中下一个要读取的位置
mix = make_item(mix, cache[cache_index % cache_size]) # 用当前哈希值和下一个到读取位置的数计算下一个哈希值
return hash(mix)
def calc_dataset(full_size, cache):
return [calc_dataset(cache, i) for i in range(full_size)]
|
- 这个
dataset 也叫作 DAG,初始大小是 1G,每隔 30000 个块更新,同时增大初始大小的 1/128 —— 8M。 - 多次调用此函数,就得到了完整的
dataset。 dataset 中的每个元素独立生成,相互之间没有联系。
矿工挖矿和轻节点验证:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| def hashimoto_full(header, nonce, full_size, dataset):
mix = hash(header, nonce)
for i in range(64):
dataset_index = get_int_from_item(mix) % full_size
mix = make_item(mix, dataset[dataset_index])
mix = make_item(mix, dataset[dataset_index + 1])
return hash(mix)
def mine(full_size, dataset, header, target):
nonce = random.randint(0, 2**64)
while hashimoto_full(header, nonce, full_size, dataset) > target:
nonce = (nonce + 1) % 2**64
return nonce
def hashimoto_light(header, nonce, full_size, cache):
mix = hash(header, nonce)
for i in range(64):
dataset_index = get_int_from_item(mix) % full_size
mix = make_item(mix, calc_dataset_item(cache, dataset_index))
mix = make_item(mix, calc_dataset_item(cache, dataset_index + 1))
return hash(mix)
|
- 轻节点临时计算出用到的
dataset 元素,矿工则是直接访问内存。
挖矿只需要块头信息,这样轻节点只需下载块头就能验证区块是否满足难度要求。
数据结构#
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
| // https://github.com/ethereum/go-ethereum/blob/v1.10.11/core/types/block.go#L68
// Header represents a block header in the Ethereum blockchain.
type Header struct {
ParentHash common.Hash `json:"parentHash" gencodec:"required"`
UncleHash common.Hash `json:"sha3Uncles" gencodec:"required"`
Coinbase common.Address `json:"miner" gencodec:"required"`
// 状态树根哈希
Root common.Hash `json:"stateRoot" gencodec:"required"`
TxHash common.Hash `json:"transactionsRoot" gencodec:"required"`
ReceiptHash common.Hash `json:"receiptsRoot" gencodec:"required"`
// 有每个 Receipt 的 Bloom 合并得到
Bloom Bloom `json:"logsBloom" gencodec:"required"`
Difficulty *big.Int `json:"difficulty" gencodec:"required"`
Number *big.Int `json:"number" gencodec:"required"`
GasLimit uint64 `json:"gasLimit" gencodec:"required"`
GasUsed uint64 `json:"gasUsed" gencodec:"required"`
Time uint64 `json:"timestamp" gencodec:"required"`
Extra []byte `json:"extraData" gencodec:"required"`
MixDigest common.Hash `json:"mixHash"`
Nonce BlockNonce `json:"nonce"`
// BaseFee was added by EIP-1559 and is ignored in legacy headers.
BaseFee *big.Int `json:"baseFeePerGas" rlp:"optional"`
}
// https://github.com/ethereum/go-ethereum/blob/v1.10.11/core/types/block.go#L158
// Block represents an entire block in the Ethereum blockchain.
type Block struct {
header *Header
uncles []*Header
transactions Transactions
// caches
hash atomic.Value
size atomic.Value
// Td is used by package core to store the total difficulty
// of the chain up to and including the block.
td *big.Int
// These fields are used by package eth to track
// inter-peer block relay.
ReceivedAt time.Time
ReceivedFrom interface{}
}
// https://github.com/ethereum/go-ethereum/blob/v1.10.11/core/types/block.go#L178
// "external" block encoding. used for eth protocol, etc.
type extblock struct {
Header *Header
Txs []*Transaction
Uncles []*Header
}
|
References

